Fourier transforms appear when limits are applied to Fourier series, which are usually a series representation of functions on a circle. Fourier transform can best be applied to handle problems with non-periodic functions. There are a lot of ordinary and partial differential equation problems which require the knowledge of Fourier transform to simplify their solutions.
We define the Fourier transform of a piecewise continuous and absolutely integrable function
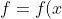)
by
}\} = \hat{f}(w) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x)e^{-iwx}{\rm d}x,)
and the inverse Fourier transform by
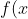 = \mathcal{F}^{-1}\{{\hat{f}(\omega)}\} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \hat{f}(\omega)e^{i\omega x}{\rm d}\omega.)
Here
|{\rm d}x)
must converge.
Now, let's look at an example.
Let
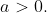
Compute the Fourier transform of
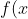 = \begin{cases} e^{-ax}, \ \text{for} \ x\ge 0 \\ e^{ax}, \ \text{for} \ x<0 \end{cases})
Solution
By definition
}\} = \hat{f}(\omega) = \sqrt{\frac{1}{2\pi}}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x)e^{-i\omega x}{\rm d}x)
x}{\rm d}x + \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-(a+i\omega)x}{\rm d}x \right])
x}}{a-i\omega} \right]_{x\to -\infty}^{x =0} + \left[ \frac{e^{-(a + i\omega)}}{-(a+i\omega)} \right]_{x=0}^{x\to \infty} \right])
 + \left(0 + \frac{1}{a+i \omega} \right) \right])


Note that
 = f(x))
x} \left\vert\right_{x\to -\infty}^{x=0} = e^{ax}.e^{-i\omega x}|_{x\to -\infty}^{x=0}, \ e^{ax} \to 0 \ \text{as} \ x \to -\infty)
The generalization to high dimensions:
https://see.stanford.edu/materials/lsof ... /chap8.pdf